What Is Domain?
Last updated on February 7th, 2026 at 02:20 am
If you’ve ever typed a website address like google.com or amazon.in, you’ve already used a domain. But what is domain exactly, and why is it so important for websites, businesses, and online branding?
In this guide, you’ll learn the meaning of a domain, how it works, its types, real examples, and how to choose the right domain name—explained in simple, beginner-friendly language.

:what Is Domain?
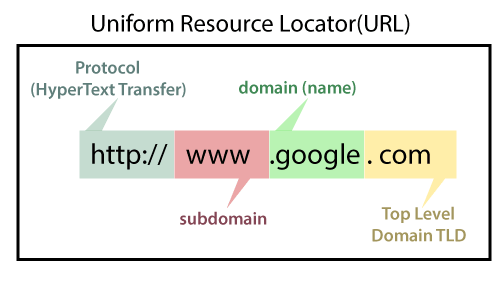
A domain is the unique web address used to identify a website on the internet. It replaces complex IP addresses with easy-to-remember names like example.com, allowing users to access websites quickly and helping brands establish a recognizable online identity.
Table of Contents
- What Is a Domain Name?
- How Does a Domain Work?
- Domain Name Example Explained
- Types of Domains
- Domain vs Hosting
- How to Choose the Right Domain Name
- Beginner-Friendly Domain Checklist
- Domain Selection Comparison Table
- FAQs
- FAQ Schema (HTML)
What Is a Domain Name?

A domain name is the human-readable address of a website. Instead of remembering numerical IP addresses like 192.168.1.1, users can simply type a domain such as example.com.
A domain typically has two main parts:
- Name: example
- Extension (TLD): .com, .in, .org, etc.
Together, they form a complete website address.
How Does a Domain Work?
Behind the scenes, domains work through a system called DNS (Domain Name System).
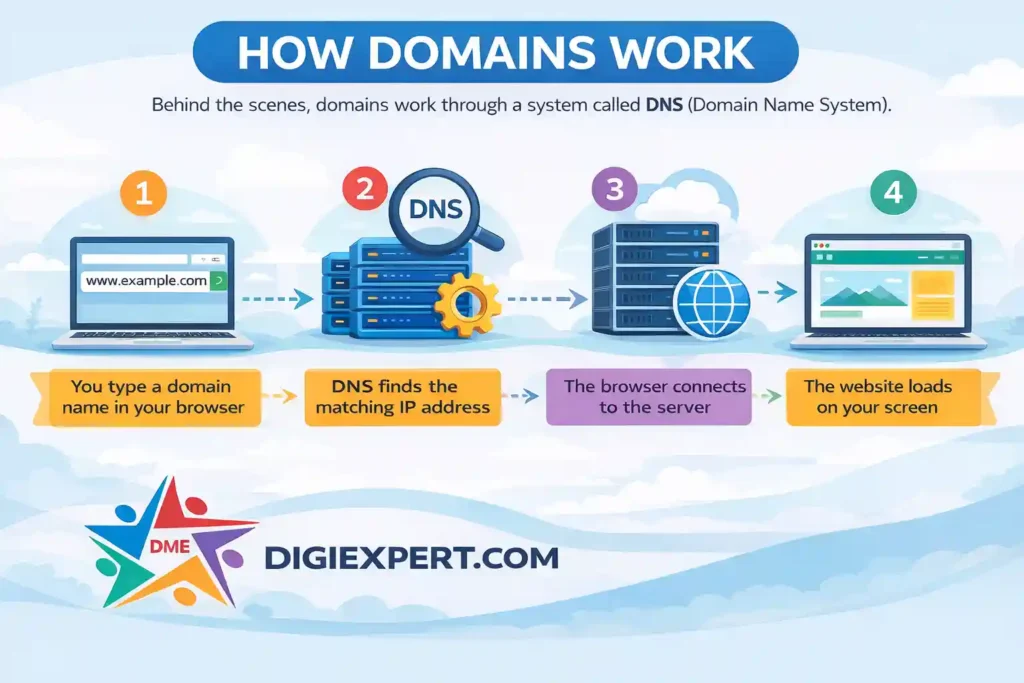
Here’s a simplified flow:
- You type a domain name in your browser
- DNS finds the matching IP address
- The browser connects to the server
- The website loads on your screen
Think of DNS as the internet’s phonebook.
Domain Name Example Explained
Let’s break down blog.example.co.in:
- .in → Country code (India)
- .co → Commercial category
- example → Brand or website name
- blog → Subdomain
Each part has a specific purpose.
Types of Domains
Understanding domain types helps you choose the right one for your website.

Top-Level Domains (TLDs)
These are the most common:
- .com (commercial)
- .org (organization)
- .net (network)
Country Code TLDs (ccTLDs)
Used for specific countries:
- .in (India)
- .uk (United Kingdom)
- .us (United States)
Subdomains
Created under a main domain:
- blog.example.com
- shop.example.com
Domain vs Hosting
Many beginners confuse these two—let’s clear it up.
| Aspect | Domain | Hosting |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Website address | Stores website files |
| Example | google.com | Server where Google lives |
| Required | Yes | Yes |
| Bought Separately | Yes | Yes |
👉 A domain points users to your hosting server.
How to Choose the Right Domain Name
Choosing the right domain is critical for SEO and branding.

Best Practices
- Keep it short and simple
- Easy to spell and pronounce
- Avoid numbers and hyphens
- Use
.comwhen possible - Reflect your brand or niche
If you’re planning to build skills around websites and online growth, learning these basics is often covered in a structured digital marketing training program that explains domains, hosting, and SEO together.
Beginner-Friendly Domain Checklist
Before buying a domain, make sure you check this list:
- ✅ Is it easy to remember?
- ✅ Is it brandable?
- ✅ No trademark issues?
- ✅ Relevant to your niche?
- ✅ Available on social media?
- ✅ SEO-friendly keywords (if possible)?
This checklist alone can save you years of rebranding trouble.
Why Domain Knowledge Matters for Digital Marketing
Domains impact:
- Brand trust
- Click-through rates
- SEO visibility
- Email credibility
If you’re serious about online careers, a professional digital marketing course in dehradun often starts with foundational concepts like domains, hosting, and website structure before moving into SEO, ads, and analytics.
For learners who want hands-on exposure, the Digiexprt digital marketing course includes practical website setup so students don’t just learn theory—they actually build and manage real domains.
FAQs
1. What is domain in simple words?
A domain is the address people type in a browser to visit a website.
2. Can two websites have the same domain?
No. Every domain name is unique worldwide.
3. Is domain free or paid?
Most custom domains are paid yearly, though some platforms offer temporary free subdomains.
4. What is the best domain extension?
.com is the most trusted, but .in, .org, and niche TLDs also work well.
5. What is a subdomain?
A subdomain is a part of the main domain used to organize content, like blog.example.com.
6. How long can I register a domain?
Domains can usually be registered from 1 to 10 years.
7. Does domain affect SEO?
Yes. A clean, relevant, and trustworthy domain can positively impact SEO.