Search Engine Optimization (SEO): Types & Techniques Guide
Last updated on January 10th, 2026 at 01:06 pm
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is the backbone of long-term online visibility. Whether you run a business website, blog, or e-commerce store, SEO helps your content appear when people actively search for solutions. In this guide, you’ll learn types of SEO, practical techniques, a beginner checklist, and FAQs—all in simple language.
What is SEO?
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is the process of improving a website’s visibility in organic (non-paid) search results by optimizing content, technical structure, and external signals. The goal is to attract relevant visitors, improve user experience, and increase conversions by matching search intent.
Table of Contents
- Why SEO Matters Today
- Types of SEO Explained
- On-Page SEO Techniques (Step-by-Step)
- Off-Page SEO Strategies That Work
- Technical SEO Checklist for Strong Foundations
- Beginner-Friendly SEO Checklist
- Common SEO Mistakes to Avoid
- FAQs
- FAQ Schema (HTML)
Why SEO Matters Today
People trust search engines. When your page ranks on the first page, you gain:
- High-intent traffic (users already looking for solutions)
- Long-term results compared to ads
- Better credibility and brand recall
- Lower customer acquisition cost over time

SEO also improves site usability, page speed, and content quality—benefits that help both users and search engines.
Types of SEO Explained
SEO is not one single task. It has three main pillars:
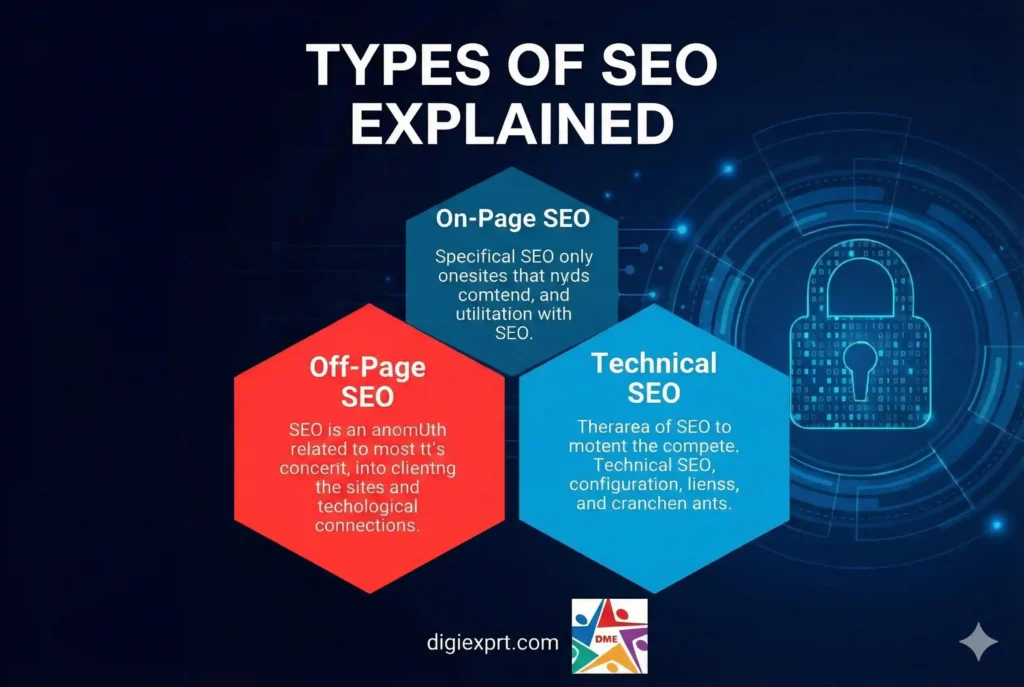
1. On-Page SEO
Optimizing content and HTML elements on your own pages:
- Keywords, headings, internal links
- Content depth and readability
- Image optimization
2. Off-Page SEO
Building authority outside your website:
- Backlinks from relevant sites
- Brand mentions
- Social sharing signals (indirect)
3. Technical SEO
Improving how search engines crawl and index your site:
- Page speed, mobile friendliness
- Clean URLs, sitemaps
- Structured data
All three must work together for stable rankings.
On-Page SEO Techniques (Step-by-Step)
These are the actions you can take directly on your pages.

1. Keyword Research with Intent
Choose keywords based on what users actually want:
- Informational (learn)
- Commercial (compare)
- Transactional (buy)
Use tools or Google suggestions to find long-tail phrases that match your content topic.
2. Optimize Title & Meta Description
- Include the main keyword naturally
- Keep title under ~60 characters
- Write benefit-driven descriptions
3. Use Proper Heading Structure
- One H1 per page (main topic)
- H2 for sections, H3 for sub-sections
- Include secondary keywords where relevant
4. Content Optimization
- Answer questions clearly
- Use bullets, examples, and steps
- Add internal links to related pages
5. Image & Media SEO
- Compress images
- Use descriptive ALT text
- Avoid heavy unoptimized videos
If you want to learn practical content and optimization skills with real projects, structured digital marketing training can shorten the learning curve and help you avoid trial-and-error.
Off-Page SEO Strategies That Work
Off-page SEO tells search engines that others trust your site.
1. Quality Backlink Building
Focus on:
- Relevant industry blogs
- Local business directories
- Guest posts with value
Avoid spammy link packages or automated tools.
2. Brand Mentions
Even without links, mentions across:
- Forums
- Social media
- News sites
can improve brand authority signals.
3. Local SEO (for Businesses)
- Optimize Google Business Profile
- Collect genuine customer reviews
- Maintain consistent NAP (Name, Address, Phone)
These steps are essential if you target city-based searches.
Technical SEO Checklist for Strong Foundations
Technical SEO ensures search engines can easily access your site.
| Area | What to Check | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Page Speed | Core Web Vitals, image size | Faster sites rank better |
| Mobile Friendly | Responsive design | Mobile-first indexing |
| Indexing | XML sitemap, robots.txt | Proper crawling |
| URL Structure | Clean, readable URLs | Better user & bot understanding |
| HTTPS | SSL certificate | Security + trust |
| Structured Data | Schema markup | Rich results in SERPs |
If technical SEO feels confusing, learning through a guided digital marketing course in dehradun with hands-on website audits can be extremely helpful for beginners.
Beginner-Friendly SEO Checklist
Use this simple list when publishing any new page:
- Choose one primary keyword
- Write helpful, original content
- Optimize title, meta, headings
- Add internal links
- Compress and tag images
- Ensure mobile friendliness
- Submit page to Search Console
- Build at least 1–2 quality backlinks
Consistency beats shortcuts in SEO.
Common SEO Mistakes to Avoid
- ❌ Keyword stuffing
- ❌ Copy-pasting content from other sites
- ❌ Ignoring mobile users
- ❌ Buying low-quality backlinks
- ❌ Publishing thin content
Search engines reward usefulness, not tricks.
FAQs
1. How long does SEO take to show results?
SEO usually takes 3–6 months for noticeable improvements, depending on competition, content quality, and technical health of the website.
2. Is SEO better than paid ads?
SEO is better for long-term growth, while ads are good for quick traffic. Many businesses use both together.
3. Can beginners learn SEO without coding?
Yes. Most SEO tasks like keyword research, content optimization, and link building don’t require coding skills.
4. What is the most important SEO factor?
There’s no single factor, but helpful content + good user experience + strong backlinks together drive rankings.
5. Is local SEO different from normal SEO?
Local SEO focuses on geographic searches and Google Maps visibility, while regular SEO targets broader organic results.
6. Do social media signals help SEO?
They don’t directly affect rankings, but they increase content reach, which can lead to more backlinks.
7. Should I learn SEO or full digital marketing?
SEO is a core part of digital marketing. Learning it along with ads, analytics, and content gives better career opportunities. Programs like the Digiexprt digital marketing course cover SEO in a practical, job-ready way.
Want to Learn SEO Practically?
If you’re serious about building real skills—not just reading theory—consider structured learning with live projects, audits, and campaign experience. A complete program covering SEO, ads, analytics, and content can help you apply what you learn faster.
You can explore a practical digital marketing training program here:
👉 https://digiexprt.com/


